In this article we shall get familiarization about the concept of Condition Based Maintenance (CBM). This approach is part of total predictive maintenance.
The CBM Philosophy focuses utilizing the Condition Monitoring technologies to predict the failure patterns of an asset.
This will allow maintenance department to scheduled the activities based on equipment condition and not operation time.
Purpose and benefits of CBM
The vision of condition based monitoring is to attain:
- Meaningful set of maintenance schedules (Technical Basis of Maintenance – TBoM)
- Improved operating performance
- Ensure safety & environmental protection
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Comprehensive maintenance database (Centralized)
- Clearer view of resource requirements CBM attains lasting benefits & can be applied across all or just selected equipment
CBM Methodology
The strategy of conditional monitoring uses a two level approach by overlaying techniques & technologies on monitored components.
Level one (Short term): Identify and reduce equipment failures across site. It uses technologies to troubleshoot and examine poor performing assets i.e. Energy usage examinations etc.
Level Two (Medium to long term): This method reduces maintenance exam tasks, extends maintenance exams and overhaul periodicities (TBoM integration). Uses technologies to reduce maintenance costs. Effective utilization of work force. Increased knowledge of asset performance and condition. Feedback into TBoM
Condition Based Maintenance Financial Impacts
Easy to Labour Low on services measure Overheads profit Reliability Safety Legislation Design Scrap out Availability Catastrophic Poor failures maintenance Breakdowns & Repairs Use of skills Warranty Low Flexibility Hard to High on measure profit
Application of Condition Based Maintenance
Oil and Grease Analysis- Three dimensions:
Wear
- Ferrous
- Nonferrous
Contamination
- Dust
- Water
- Fuel
Chemistry
- Oil
- Additive
Portable Vibration Analysis
What does it monitor?
- Imbalance Problems
- Mis-alignment Problems
- Bearing Problems
- Electrical Defects
Where?
- Cranes
- Air Compressor motors
- Brake resistor / Traction cooling fans
- HVAC equipment
- Alternators
- Turbo charger
- Gearboxes (wheel lathe)
- Electrical motors
- Cooling system pumps
- Lubrication oil system pumps
- Fuel Pumps
- Diesel Engine
- Axle boxes
Portable Ultrasonic Analysis
What does it monitor?
- Air Leak Problems
- Electrical Problems
- Mechanical Problems
Location?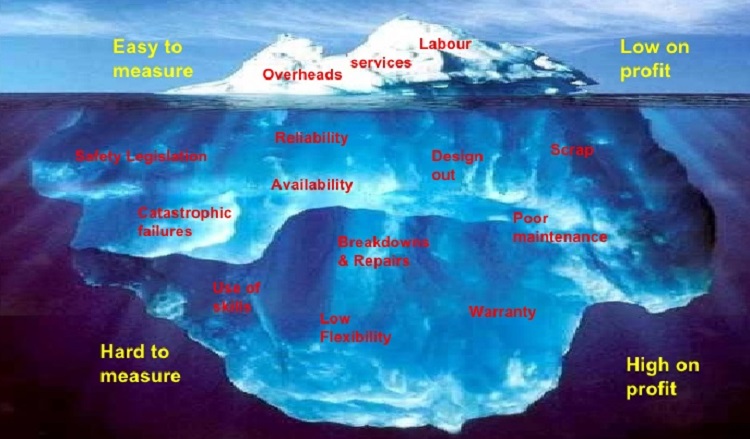
Leak Detection
- Valves
- Air supply lines
- Flexible hoses
- Pneumatic systems
- Pressurized systems Electrical
- Vacuum system problems
- Electrical- Arcing Detection
- Compressor Mechanical
- Steam Traps
Mechanical
- Bearing defects
- Lack of Lubrication
- Over Lubrication
Portable Thermography Analysis
What does it monitor?
- Electrical Problems
- Mechanical Problems
- Pipework Problems
Problems detected?
- Electrical Problems
- High resistance connection
- Corroded / hot connections
- Earth returns – Higher loading
- Relay problems
- Internal fuse damage
- Internal circuit breaker fault
- Cracking insulation
- Overload or unbalanced load
- Busbar faults
- Couplings
- Cooling jackets


